Cancer Info
Brain Cancer
How common are Brain cancers in India?
Brain cancers are relatively rare compared to other types of cancers, but their incidence is gradually increasing in India. According to data, the annual incidence is about 2 to 5 per 100,000 people. Certain types, like gliomas and meningiomas, are more commonly diagnosed. While overall rates are lower than in some Western countries, awareness and diagnostic capabilities are improving.
What are the main risk factors for brain cancers?
Several risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing brain cancer, including:
Genetic Factors: Conditions like neurofibromatosis and Li-Fraumeni syndrome increase risk.
Exposure to Radiation: Previous radiation therapy to the head increases risk.
Family History: Having a family member with brain cancer can slightly elevate your risk.
Age: Some types of brain cancer are more common in children and older adults.
How are brain cancers investigated ?
Currently, there are no standard screening tests for brain cancer in asymptomatic individuals. However, if symptoms suggestive of brain cancer are present, doctors may recommend:
MRI Scans: These provide detailed images of the brain and can identify tumors.
CT Scans: Useful for detecting bleeding or structural changes in the brain.
What are the signs and symptoms of brain cancer?
Common signs and symptoms include:
Headaches: Persistent or worsening headaches that may be different from usual patterns.
Seizures: New-onset seizures, particularly in adults.
Cognitive Changes: Memory problems, confusion, or changes in personality.
Vision or Hearing Problems: Blurred vision, double vision, or hearing difficulties.
Weakness or Numbness: On one side of the body or in the limbs.
Does smoking or alcohol use affect the risk of brain cancer?
While smoking is a known risk factor for many cancers, its direct link to brain cancer is less clear. Some studies suggest a potential association, but more research is needed. Alcohol consumption does not have a well-established connection with brain cancer, but excessive use can affect overall health and well-being.
What about mobile phone radiation? Does it cause brain cancer?
Current research does not provide conclusive evidence linking mobile phone use to brain cancer. While some studies suggest a potential risk, major health organizations, including the WHO, state that more research is needed. It is advisable to use hands-free devices to minimize direct contact with the head.
What investigations are done to diagnose brain cancer?
Diagnosis typically involves:
Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans to visualize the brain and detect tumors.
Biopsy: A tissue sample may be taken from the tumor to determine its type.
Neurological Exams: Assessing cognitive function, reflexes, and coordination.
How is brain cancer managed based on its stage?
Management strategies vary based on the tumor’s type, location, and stage:
Early Stage: Surgery to remove the tumor may be the primary treatment.
Advanced Stage: Treatment may involve a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
What are molecular tests, and why are they important?
Molecular tests analyze the genetic characteristics of the tumor. They help identify specific mutations that can guide targeted therapy options. Understanding these genetic features can improve treatment effectiveness and personalize care for each patient
What is targeted therapy for brain cancer?
Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically attack cancer cells based on their unique molecular characteristics. For certain types of brain tumors, targeted therapies can block signals that promote tumor growth, potentially leading to better outcomes with fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
How does chemotherapy play a role in brain cancer treatment?
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. It is often used for more aggressive tumors or when surgery is not feasible. While effective, chemotherapy can cause side effects like nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. The treatment plan is tailored to the individual’s specific tumor type and overall health.
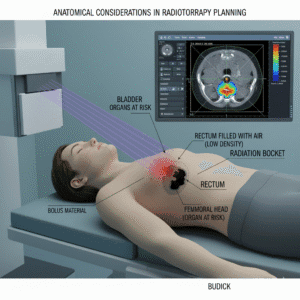
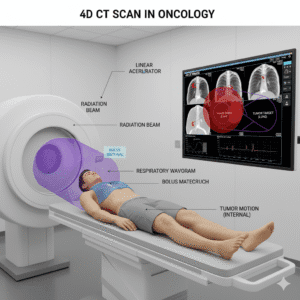
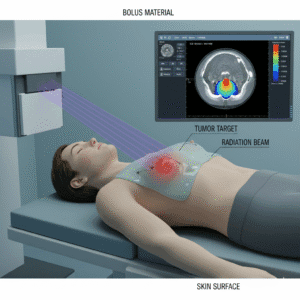
What is the role of radiotherapy in treating brain cancer?
Radiotherapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It can be used:
After Surgery: To eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
For Inoperable Tumors: When surgery isn’t an option.
Palliation: To relieve symptoms in advanced cases. Side effects may include fatigue and skin irritation.
What is CyberKnife radiosurgery, and when is it used?
CyberKnife is a form of stereotactic radiosurgery that delivers
highly focused radiation to tumors. It is particularly beneficial
for:
Small,
well-defined tumors: CyberKnife can treat tumors without the
need for open surgery.Inoperable
Tumors: It provides a non-invasive option for patients unable to
undergo traditional surgery.Cyberknife treatment offers many advantages –
Precision: Targets tumors accurately, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Fewer Sessions: Often requires only a few treatment sessions compared to traditional radiation.
Quick Recovery: Many patients can return to normal activities shortly after treatment.
What role does immunotherapy have in treating brain cancers?
Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. For certain brain tumors, like glioblastomas, immunotherapy may be used to enhance immune response against tumor cells. While still an area of active research, promising results have been seen in some clinical trials.
What should patients expect during follow-up appointments?
Follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring recovery and detecting any signs of recurrence. These visits may involve:
Physical and Neurological Exams: Assessing overall health and cognitive function.
Imaging Tests: Regular MRI or CT scans to check for tumor regrowth.
Blood Tests: To monitor overall health and liver function.
How do genetics play a role in brain cancer?
Certain genetic mutations can predispose individuals to brain cancers. Genetic counseling and testing can provide valuable information about personal risk and potential implications for family members.
What role does exercise & rehabilitation play in recovery from brain cancer?
Regular physical activity can support recovery by improving overall health, reducing fatigue, and enhancing mood. Tailored exercise programs can help patients regain strength and mobility after treatment.
Rehabilitation may include:
Physical Therapy: To improve strength and coordination.
Occupational Therapy: To help patients regain independence in daily activities.
Speech Therapy: For those experiencing communication difficulties or swallowing issues.
How can diet and nutrition support brain cancer patients?
A balanced diet is essential for recovery. Patients should focus on:
Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins and antioxidants.
Whole Grains: For sustained energy.
Lean Proteins: To support tissue repair.
Consulting a nutritionist can help tailor dietary recommendations based on individual needs and treatment side effects.
Can brain cancer affect driving abilities?
Yes, brain cancer and its treatments can affect cognitive function, vision, and motor skills, which may impair driving abilities. It’s important for patients to discuss their specific situation with their healthcare provider and consider local laws regarding driving post-treatment.
How is seizure management handled in brain cancer patients?
Seizures are common in brain cancer patients and may be managed with:
Antiepileptic Medications: To control seizure activity.
Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding triggers and maintaining a regular schedule. Patients should report any seizure activity to their healthcare provider for appropriate management.
What impact does brain cancer have on memory?
Brain cancer can affect memory due to tumor location, treatment effects, or stress. Cognitive rehabilitation strategies, including memory exercises and support from professionals, can help improve memory function and coping strategies.