Cancer Info
Uterine cancer
What is the incidence of endometrial cancer in India?
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecological cancer in India, especially among postmenopausal women. Its incidence has been rising, attributed to factors such as increased obesity, lifestyle changes, and hormonal factors. Awareness about the disease and its symptoms is crucial for early detection and better outcomes.
What are the risk factors for endometrial cancer?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing endometrial cancer:
- Obesity: Excess body weight is a significant risk factor, as fat tissue produces estrogen, which can promote the growth of the endometrium.
- Age: Most cases occur in women over 50, particularly after menopause.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions that cause unopposed estrogen exposure, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can increase risk.
- Diabetes: Women with diabetes have a higher risk of endometrial cancer.
- Family History: A family history of endometrial or other cancers can raise individual risk.
- Early Menstruation and Late Menopause: Early onset of menstruation and late onset of menopause can increase exposure to estrogen.
How is endometrial cancer screened for?
Currently, there is no routine screening test for endometrial cancer like there is for cervical cancer. However, women should be vigilant about changes in menstrual patterns or any unusual bleeding, especially after menopause. Healthcare providers may recommend transvaginal ultrasound or endometrial biopsy if symptoms arise.
What are the signs and symptoms of endometrial cancer?
Common signs and symptoms include:
- Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: This may include bleeding between periods or heavy bleeding during periods. Postmenopausal bleeding is particularly concerning.
- Pelvic Pain: Persistent pain in the pelvic region may occur.
- Unusual Vaginal Discharge: Changes in discharge, such as a watery or bloody discharge.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can sometimes be a symptom.
What is the role of oral contraceptive pills (OCP) and hormones in endometrial cancer?
Oral contraceptive pills (OCP) can actually reduce the risk of endometrial cancer, especially with long-term use. They help regulate hormonal levels and reduce unopposed estrogen exposure. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), particularly with estrogen alone, can increase the risk if not balanced with progesterone. Women considering HRT should discuss the risks and benefits with their doctor
How do fibroids and polyps relate to endometrial cancer?
- Fibroids: These non-cancerous growths in the uterus can cause heavy bleeding and discomfort but are not directly linked to cancer. However, they can complicate the diagnosis and management of endometrial cancer.
- Polyps: These are small growths on the endometrial lining. While most polyps are benign, certain types can have a higher risk of becoming cancerous, especially in postmenopausal women. Regular monitoring and removal may be necessary.
What is the impact of smoking and alcohol on endometrial cancer risk?
Smoking is a known risk factor for various cancers, including endometrial cancer. It may influence hormone levels and increase risk. Alcohol consumption may also contribute to risk, particularly when combined with other factors like obesity and hormonal imbalances. Reducing or eliminating smoking and moderating alcohol intake can be beneficial for overall health.
What investigations are done to diagnose endometrial cancer?
Diagnosis typically involves several tests:
- Pelvic Examination: A thorough check of the reproductive organs.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: This imaging test helps visualize the uterus and assess the thickness of the endometrial lining.
- Endometrial Biopsy: A small sample of the endometrial tissue is taken and examined for cancer cells. This is a key diagnostic tool.
Hysteroscopy: A procedure to look inside the uterus using a thin, lighted tube, often used to remove tissue samples
What is stage-wise management for endometrial cancer?
Management is based on the cancer stage:
- Stage I: Cancer is confined to the uterus. Treatment usually involves a total hysterectomy (removal of the uterus and cervix) and may include lymph node evaluation.
- Stage II: Cancer has spread to the cervix. Treatment often includes surgery, likely followed by radiation therapy.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread beyond the uterus to nearby tissues or lymph nodes. Management may involve surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
- Stage IV: Advanced cancer that has spread to distant organs. Treatment may focus on chemotherapy or immunotherapy and short course radiotherapy and palliative care.
What are molecular tests, and why are they important?
Molecular tests analyze the genetic characteristics of cancer cells. In endometrial cancer, these tests can identify specific mutations or changes that may influence treatment options. For instance, certain mutations might suggest a better response to targeted therapies, allowing for more personalized and effective treatment plans.
What role does chemotherapy play in treating endometrial cancer?
Chemotherapy is often used for advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer. It involves using drugs to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells throughout the body. Common regimens may include a combination of carboplatin and paclitaxel. Side effects can include nausea, fatigue, hair loss, and an increased risk of infections.
How does immunotherapy work for endometrial cancer?
Immunotherapy helps the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. For certain types of endometrial cancer, particularly those with specific genetic markers, immunotherapy (like immune checkpoint inhibitors) can be an effective treatment option. It can enhance the body’s natural ability to fight cancer, potentially leading to better outcomes. It is usually advised in stage 4 cancer, that when it has spread to other organs.
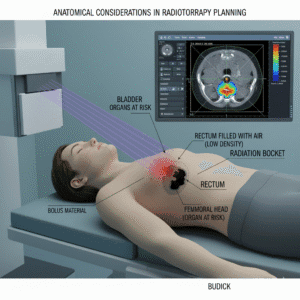
What is the role of radiotherapy in treating endometrial cancer?
Radiotherapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It can be used:
- Post-Surgery: To eliminate any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Primary Treatment: For patients who may not be surgical candidates.
- Palliative Care: To relieve symptoms in advanced cases. Side effects may include fatigue and localized skin irritation.
What is CyberKnife radiosurgery, and what are its benefits? Is there a role in endometrial cancers?
CyberKnife is a non-invasive treatment that delivers precise radiation to tumors. Benefits include:
- Non-Invasive: No surgical incisions required.
- Precision Targeting: Real-time imaging allows for accurate targeting while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Short Treatment Course: Typically completed in a few sessions.
- Minimal Side Effects: Generally fewer side effects compared to traditional radiation therapy.
There are trials exploring the role of CyberKnife in these tumours currently but currently can be offered to patients who have relapsed after primary treatment. Consult your Radiation Oncologist.
How does genetics play a role in endometrial cancer risk?
Genetics can significantly influence the likelihood of developing endometrial cancer:
Certain inherited conditions, such as Lynch syndrome (also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer or HNPCC), are linked to a higher risk of endometrial cancer and other cancers. Genetic counseling can be beneficial for individuals with a family history of cancer. During counseling, healthcare professionals can assess your risk factors, provide information about genetic testing, and discuss the implications for you and your family. Understanding your genetic risk can also guide decisions regarding screening and preventive measures.
Why are follow-up appointments important after endometrial cancer treatment?
Follow-up appointments are crucial for several reasons:
These visits help monitor your recovery and ensure that you are healing properly after treatment. During follow-ups, your doctor will perform physical examinations to check for any signs of recurrence, such as unusual symptoms or physical changes. Imaging tests, like ultrasounds or CT scans, may be ordered to visualize the uterus and surrounding areas, while blood tests can help assess hormone levels and check for tumor markers. Regular follow-up helps in early detection of any potential issues, allowing for timely intervention if needed.
How can I improve my chances of recovery after the treatment gets over?
Regular physical activity is essential for overall health and recovery:
Engaging in safe, moderate exercise can help maintain a healthy weight, which is particularly important for endometrial cancer survivors, as obesity is a known risk factor for recurrence. Exercise can also improve your mood, boost energy levels, and enhance your physical fitness. Activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can be great options. It’s important to consult your healthcare provider before starting any exercise program to ensure it aligns with your recovery plan.
Rehabilitation services can significantly aid in recovery:
After treatment, especially if surgery has affected your mobility or physical function, rehabilitation can provide support. Physical therapy may focus on exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and balance. Counseling services can also be beneficial for addressing emotional and psychological challenges that may arise during recovery. Overall, rehabilitation aims to help you regain independence and improve your quality of life.
A balanced diet is vital for recovery and overall well-being:
Nutrition plays a crucial role in healing and maintaining energy levels. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support your body during recovery. Nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can aid in healing and boost your immune system. Consulting with a registered dietitian can provide personalized dietary recommendations tailored to your needs and preferences, ensuring you get the necessary nutrients for optimal recovery.
What should I know about the impact of endometrial cancer treatment on sex and fertility?
Endometrial cancer treatments can affect sexual function and fertility:
Surgery, radiation, and certain medications can influence hormone levels, leading to changes in libido, vaginal dryness, or discomfort during intercourse. It’s essential to discuss any concerns regarding sexual health with your healthcare provider, as they can suggest ways to manage these issues. Additionally, if you are considering having children in the future, discussing fertility preservation options before treatment can be crucial, as some treatments may impact your ability to conceive.
Family planning is an important consideration after treatment for endometrial cancer:
It’s vital to discuss your future family planning goals with your healthcare team. They can provide insights into the risks and considerations based on your treatment history and individual health. Depending on the extent of your treatment and any hormonal changes, there may be specific recommendations regarding contraceptive options or the timing of future pregnancies. Ensuring open communication with your healthcare provider will help you make informed decisions that align with your personal and family goals.
Many women can have successful pregnancies after endometrial cancer, but careful planning is necessary:
If you have undergone treatment, it’s essential to discuss your individual circumstances with your healthcare provider. Factors such as the type of treatment, your overall health, and the stage of cancer can influence pregnancy outcomes.
Toggle Title
Toggle Content