Cancer Info
What are plasma cell disorders?
Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects plasma cells, a type of white blood cell responsible for producing antibodies. In myeloma, these cells become malignant and multiply uncontrollably, leading to various health issues, including bone pain, anemia, and kidney problems.
How common is multiple myeloma in India?
Multiple myeloma is relatively rare but increasing in incidence. It accounts for about 1-2% of all cancers in India, with approximately 5,000 new cases diagnosed each year. It typically affects older adults, with most patients diagnosed in their 60s or 70s.
What are the symptoms of multiple myeloma?
Common symptoms include:
- Bone pain, particularly in the back or ribs
- Fatigue and weakness
- Anemia (low red blood cell count)
- Frequent infections
- High calcium levels, leading to thirst and frequent urination
- Kidney dysfunction
How is multiple myeloma diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves several tests:
- Blood tests: To check for abnormal proteins (like M-proteins), kidney function, and blood cell counts.
- Urine tests: To detect Bence Jones proteins, which are produced by myeloma cells.
- Bone marrow biopsy: A sample is taken to look for abnormal plasma cells.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans are used to identify bone damage or lesions.
What blood investigations are done for myeloma?
Key blood tests include:
- Complete blood count (CBC): Checks levels of red and white blood cells and platelets.
- Serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP): Identifies abnormal proteins produced by myeloma cells.
- Beta-2 microglobulin and albumin levels: Help in assessing disease prognosis.
- Calcium levels: To check for hypercalcemia, common in myeloma.
Kidney function tests: To evaluate kidney health
How do doctors determine the stage of myeloma?
Staging of multiple myeloma is commonly done using the Durie-Salmon system or the International Staging System (ISS), which considers:
- The amount of monoclonal protein in the blood
- The level of calcium in the blood
- Hemoglobin levels
- The number of bone lesions seen on X-ray or MRI
What is the management based on staging?
Management strategies vary by stage:
- Stage I: May involve monitoring or early treatment with targeted therapies.
- Stage II: Often treated with a combination of chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and possibly stem cell transplantation.
- Stage III: Typically requires more aggressive treatment, including high-dose chemotherapy followed by stem cell transplantation.
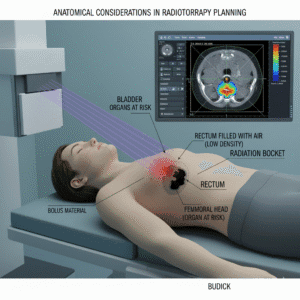
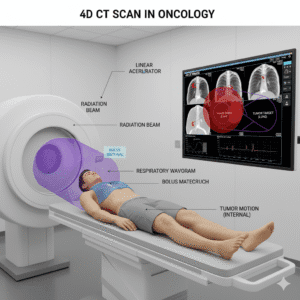
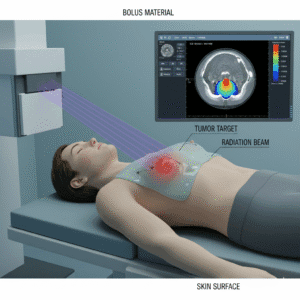
How are plasmacytomas or myelomas managed with radiotherapy alone?
Plasmacytomas are localized tumors of abnormal plasma cells. If they are solitary and do not involve the bone marrow, they may be treated with radiotherapy alone. This can effectively shrink the tumor and relieve symptoms. Radiotherapy is often used to target specific areas affected by plasmacytomas or to alleviate pain in bones affected by myeloma. It can also help reduce tumor size before other treatments. Radiotherapy is now extensively being used all over the world as a part of bone marrow transplantion.
What role does surgery play in myeloma treatment?
Surgery is not typically used to treat multiple myeloma directly, but it may be employed to relieve pressure from tumors or to stabilize bones that are weakened by myeloma lesions (bone fixation).
What about chemotherapy and immunotherapy for multiple myeloma?
Chemotherapy is the mainstay treatment for myelomas. It uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. It is often part of the treatment regimen for multiple myeloma, usually in combination with other therapies like immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy helps the immune system recognize and attack myeloma cells. It includes monoclonal antibodies and other treatments that can enhance the immune response against the cancer.
What types of bone marrow transplantation are there?
There are two main types of bone marrow transplantation:
- Autologous transplant: The patient’s own stem cells are collected and reinfused after high-dose chemotherapy.
- Allogeneic transplant: Stem cells are sourced from a donor. This option is usually considered for more aggressive myeloma.
The duration typically ranges from 2-6 weeks in the hospital, followed by outpatient follow-up for several months. The cost in India can vary widely, ranging from ₹15 lakhs to ₹40 lakhs, depending on the type of transplant and hospital facilities.
What is the role of total body radiotherapy in bone marrow transplantation?
Total body radiotherapy (TBI) is part of the conditioning regimen before an allogeneic transplant. It helps eliminate cancer cells and suppress the immune system to allow the new stem cells to engraft.
What are the control and survival rates for multiple myeloma?
With advancements in treatment, many patients experience good control of the disease. The overall 5-year survival rate for multiple myeloma has improved and now ranges between 50-70%, depending on the stage and treatment response.
What does rehabilitation involve after myeloma treatment?
Rehabilitation focuses on physical and emotional recovery. It may include:
- Physical therapy to regain strength and mobility
- Nutritional counseling to support recovery
- Psychological support to manage emotional health and stress.
How often should I have follow-ups after treatment?
Regular follow-ups are crucial and typically occur every 3-6 months for the first few years, then annually. Follow-ups include blood tests, imaging studies, and physical exams to monitor for recurrence or manage side effects.
Follow-up investigations may include:
- Blood tests (CBC, SPEP) to check for disease markers.
- Imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, or CT scans) to look for new bone lesions or other issues.
- Urine tests to monitor protein levels.