chemoport
Q1: What is a Chemoport?
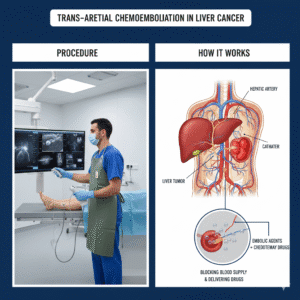
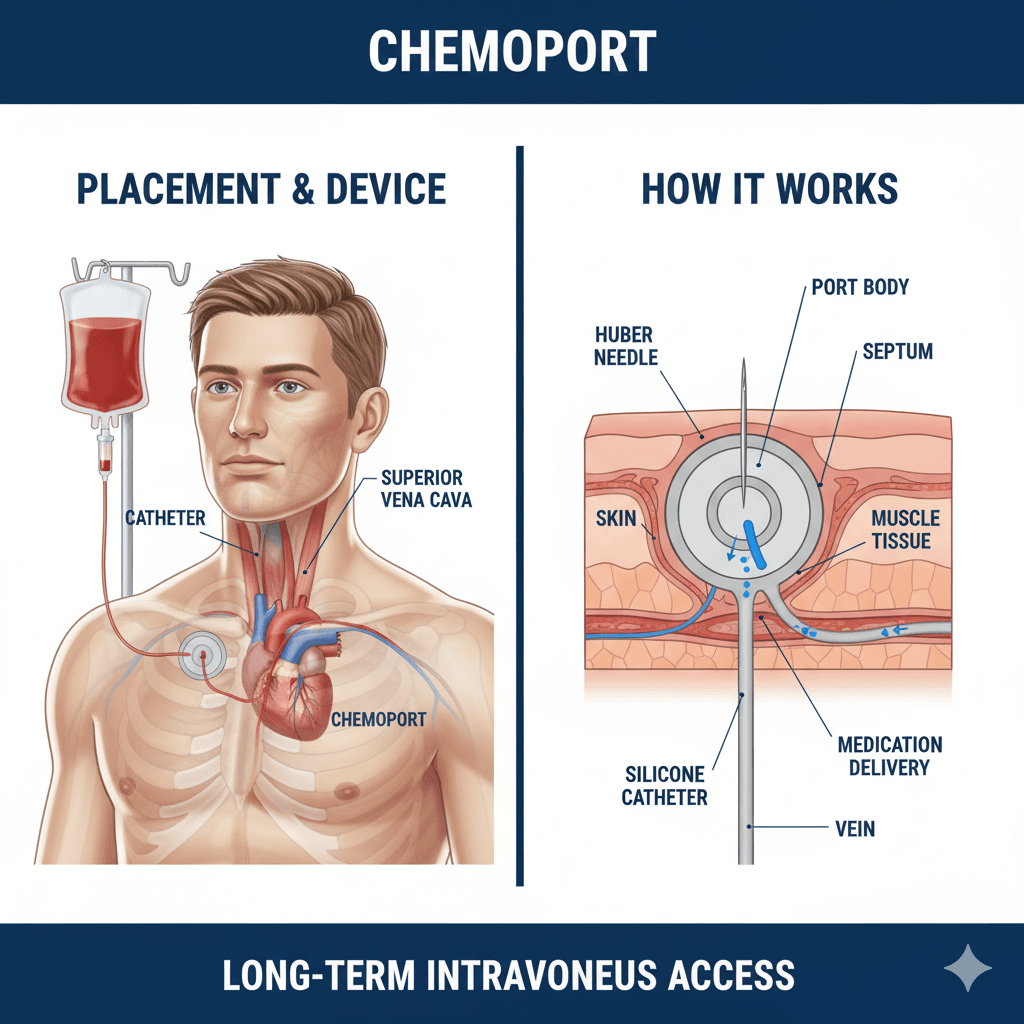
A chemoport, also known as an implanted port or port-a-cath, is a small medical device that is surgically placed under the skin to provide easy access to veins for administering chemotherapy and other medications. It consists of a reservoir (port) connected to a thin, flexible tube (catheter) that is inserted into a large vein, usually near the chest. The port can be used to deliver chemotherapy, draw blood, and give other intravenous treatments.
Q2: How does a Chemoport work?
The chemoport is implanted under the skin, typically in the upper chest area. The catheter is threaded through a vein until it reaches a larger vein near the heart. Once in place, the port allows healthcare providers to access the bloodstream by inserting a special needle into the port’s reservoir. This access point makes it easier to deliver treatments directly into the bloodstream and reduces the need for repeated needle sticks in the veins of the arms or hands.
Q3: Why is a Chemoport used in cancer treatment?
A chemoport is used in cancer treatment for several reasons:
- Convenience: It provides a stable and reliable access point for administering chemotherapy, blood transfusions, and other medications without repeatedly sticking the veins in the arms or hands.
- Comfort: The port reduces the discomfort and stress of frequent needle sticks, especially for patients who require long-term treatment.
- Reduced vein damage: Chemotherapy drugs can be harsh on veins, and using a port helps prevent damage to smaller veins, reducing the risk of vein irritation or collapse.
- Multiple uses: The port can be used for blood draws and other treatments, making it a versatile tool in cancer care.
Q4: How is a Chemoport implanted?
The implantation of a chemoport is a minor surgical procedure that usually takes place in an outpatient setting. The steps include:
- Preparation: The patient receives local anesthesia and sometimes mild sedation. The area where the port will be placed is cleaned and sterilized.
- Implantation: The surgeon makes a small incision in the chest to create a pocket under the skin for the port. The catheter is then threaded through a vein to the heart, and the port is connected to the catheter.
- Closure: The incision is closed with stitches or surgical glue, and the port is placed under the skin. A dressing is applied over the incision.
The procedure typically takes about 30 to 60 minutes, and most patients can go home the same day.
Q5: What should I expect after getting a Chemoport?
After the port is implanted, you may experience some soreness, swelling, or bruising at the incision site, which usually subsides within a few days. The port will need to be accessed and flushed regularly to keep it open and functional. Your healthcare team will provide instructions on how to care for the port and what signs of infection or complications to watch for.
Q6: How is the Chemoport used during treatment?
During treatment, a special needle is inserted into the port’s reservoir to access the catheter. This allows healthcare providers to administer chemotherapy, draw blood, or give other medications directly into the bloodstream. The port can be used for each treatment session, making it more convenient and less painful than repeated needle sticks in the arm.
Q7: How long can a Chemoport stay in place?
A chemoport can remain in place for months or even years, depending on the duration of your treatment. It can be used as long as it is functioning well and free of complications like infection. Once treatment is completed, the port can be surgically removed in a simple outpatient procedure.
Q8: What are the potential risks or complications of a Chemoport?
While chemoports are generally safe, there are some potential risks, including:
- Infection: The port site can become infected, requiring treatment with antibiotics or removal of the port.
- Clotting: Blood clots can form in the catheter, which may need to be treated with medication or by flushing the port.
- Discomfort: Some patients may experience discomfort or pain around the port site.
- Catheter issues: The catheter may become dislodged or blocked, which can require medical attention.
Your healthcare team will provide instructions on how to care for your port and minimize these risks.
Q9: How do I care for my Chemoport?
Caring for a chemoport involves keeping the port site clean and dry, watching for signs of infection, and having the port flushed regularly by a healthcare provider to prevent clotting. Your healthcare team will provide specific instructions on how to care for the port, including what activities to avoid and when to seek medical attention if problems arise.
If you have more questions about using a chemoport in your cancer treatment or need help understanding how it might fit into your care plan, talk to your healthcare provider. They can provide detailed information and guide you through the process of using and caring for a chemoport.
Related Post

CyberKnife
August 6, 2024
Immunotherapy
August 7, 2024
MRI Linac
August 7, 2024
Gamma Knife
August 7, 2024
Cancer Screening
August 22, 2024
Gallery
Click below to book a clinic appointment
Ask More Questions Send Query On Email