Cancer Info
Head and Neck Cancer
How common is head and neck cancer and what are the risk factors ?
Head and neck cancers are relatively common worldwide, accounting for about 6% of all cancers. Globally, the incidence is higher in regions where tobacco and alcohol use is prevalent, as well as where certain viral infections (like HPV) are more common. Other factors include poor oral hygiene, exposure to certain chemicals (like those in the workplace), and previous radiation treatment to the head and neck.
In India, head and neck cancers are particularly significant, making up nearly 30% of all cancers diagnosed in the country. The demographic most affected includes middle-aged and older adults, with a higher prevalence among men, largely due to higher rates of tobacco and alcohol consumption. In India, specific types of head and neck cancers, such as oral cavity cancers, are notably high due to widespread betel quid and chewing tobacco use
How can I get screened for head and neck cancers?
Currently, there isn’t a standardized screening test like a
mammogram for breast cancer. However, regular visits to a dentist can help
catch early signs of head and neck cancers, such as unusual lumps or sores in
the mouth. A healthcare provider can perform a thorough physical examination of
the head and neck during routine check-ups, looking for abnormalities.
What tests are done to diagnose head and neck cancers?
Diagnosis often starts with a clinical evaluation, where the doctor will assess symptoms and conduct a physical examination. Imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans may be ordered to get detailed pictures of the area. A biopsy, which involves removing a small sample of tissue for laboratory analysis, is typically the definitive test for confirming the presence of cancer.
What role does chemotherapy play in treatment?
Chemotherapy involves the use of powerful drugs to target and kill cancer cells. It can be administered before surgery to shrink tumors (neoadjuvant chemotherapy), after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells (adjuvant chemotherapy), or as the primary treatment if surgery isn’t feasible due to the cancer’s stage or location. The specific regimen depends on the cancer type and individual patient factors.
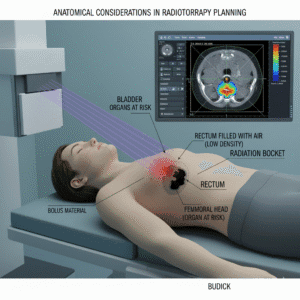
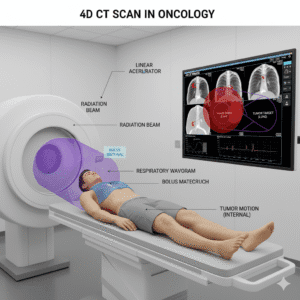
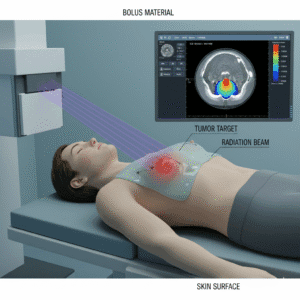
How does radiotherapy work?
Radiotherapy uses high-energy radiation to damage the DNA of cancer cells, inhibiting their ability to grow and divide. It can be used as a primary treatment, post-surgery, or in combination with chemotherapy. The treatment is typically delivered in small doses over several sessions to minimize harm to surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may experience side effects, such as fatigue or skin irritation, which are usually manageable
Will I need surgery?
Surgery is often a key component of treatment for head and neck cancers, especially when the tumor is localized. The type of surgery can vary from removing a small tumor to larger procedures that may involve reconstructing parts of the mouth or throat. The decision to pursue surgery depends on various factors, including the cancer’s size, location, and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes
What can I expect during follow-up appointments?
Follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring recovery and checking for signs of cancer recurrence. These visits typically include physical examinations and may involve imaging tests like scans. Your doctor will also discuss any ongoing symptoms or side effects from treatment, adjusting your care plan as necessary to support your health.
Are there genetic factors involved in head and neck cancers?
Yes, genetics can play a role in the development of head and neck cancers. Certain inherited genetic mutations may increase the risk, particularly if there is a family history of these cancers or related conditions. Genetic counseling can provide insights into your individual risk and guide decisions about screening and prevention strategies.
How important is exercise during treatment?
Staying active during treatment can significantly improve quality of life. Regular exercise helps combat fatigue, enhances mood, and can aid in recovery. Light activities, such as walking or stretching, are usually encouraged, but it’s important to consult your healthcare team for personalized recommendations based on your treatment plan and physical condition.
What rehabilitation services are available?
Rehabilitation can be essential for recovery after treatment. Speech therapy can help if you experience difficulty with speaking or swallowing. Physical therapy can assist in regaining strength and mobility, while nutritional counseling can provide guidance on maintaining a healthy diet, especially if you’re facing challenges related to eating due to treatment side effects.
What should I eat during treatment?
Maintaining a nutritious diet is vital during cancer treatment. Focus on a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including colorful fruits and vegetables, lean proteins (like chicken, fish, and legumes), whole grains, and healthy fats. Staying hydrated is also crucial, especially if you’re experiencing side effects like dry mouth or nausea. Consider small, frequent meals if your appetite is affected.
Are there foods I should avoid?
Certain foods can irritate your mouth and throat during treatment. It’s advisable to steer clear of spicy, acidic, or crunchy foods that may cause discomfort. Limiting alcohol and tobacco is also essential, as they can exacerbate side effects and interfere with healing.
Can stress affect my cancer treatment?
Yes, stress can negatively impact your overall health and potentially affect treatment outcomes. High levels of stress can influence your immune system and hinder recovery. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or support groups can help manage anxiety and improve your emotional well-being during this challenging time.
How can I manage side effects of treatment?
Managing side effects requires a collaborative approach with your healthcare team. Medications may be prescribed to alleviate nausea, pain, or other symptoms. Additionally, your doctor may recommend lifestyle adjustments, such as mouth rinses for sores, dietary changes to ease swallowing difficulties, or relaxation techniques to help manage stress and discomfort.