Trans arterial Chemoembolization in liver cancer
Q1: What is Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE)?
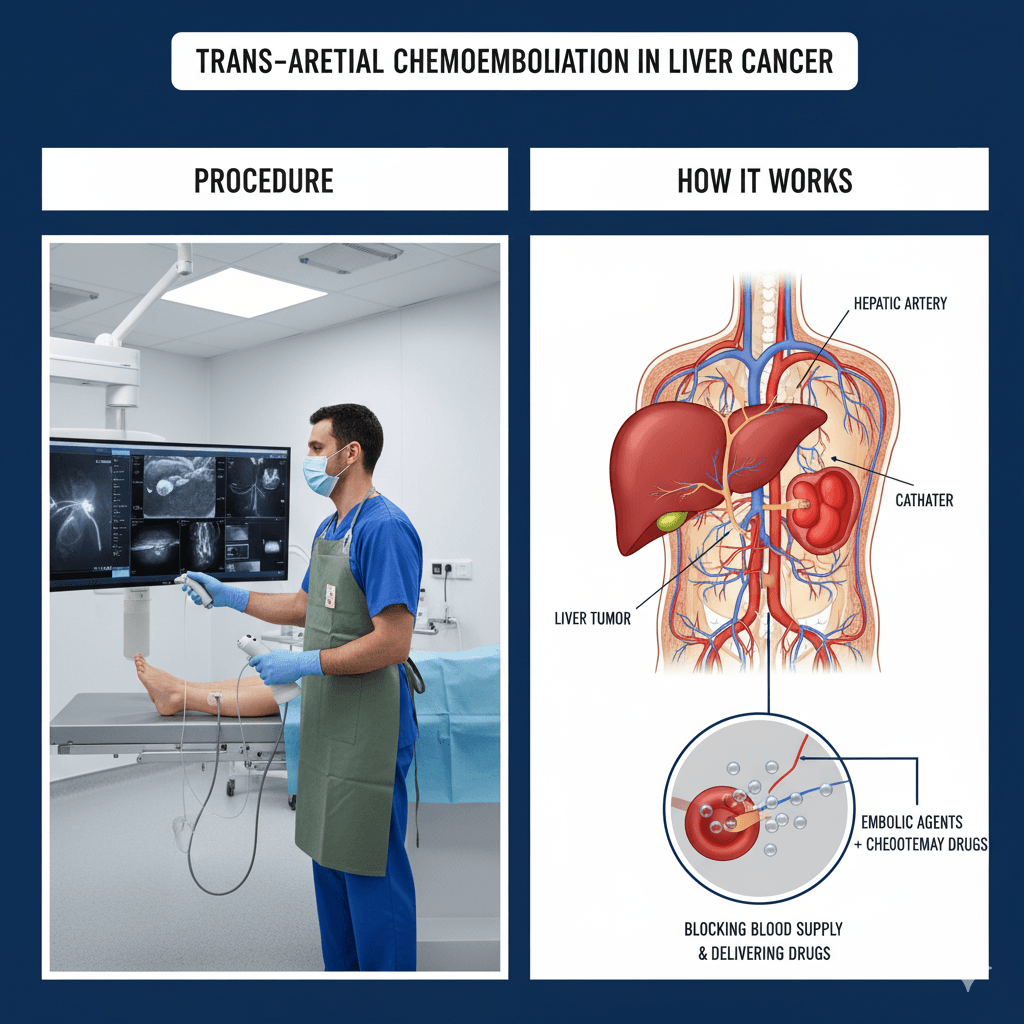
A: Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) is a minimally invasive cancer treatment that combines chemotherapy and embolization. It is used primarily to treat liver cancer. In TACE, chemotherapy drugs are delivered directly to the tumor through the blood vessels, and then the blood supply to the tumor is blocked (embolized). This dual approach increases the concentration of chemotherapy in the tumor while reducing its blood supply, leading to more effective tumor shrinkage.
Q2: How does TACE work in treating cancer?
A: TACE works by delivering chemotherapy drugs directly to the liver tumor through a catheter inserted into the hepatic artery, the main blood vessel supplying the liver. Once the chemotherapy is delivered, tiny particles are injected into the artery to block it. This embolization cuts off the blood flow to the tumor, trapping the chemotherapy drugs in the tumor and depriving it of the oxygen and nutrients it needs to grow. The combination of high-dose chemotherapy and reduced blood supply helps to shrink the tumor more effectively than systemic chemotherapy alone.
Q3: What types of cancer can be treated with TACE?
A: TACE is most commonly used to treat liver cancers, including:
- Primary liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma or HCC): TACE is a standard treatment for patients with HCC, especially when the tumor is too large for surgery or in cases where the cancer has not spread outside the liver.
- Metastatic liver cancer: TACE can also be used to treat cancers that have spread to the liver from other parts of the body, such as colorectal cancer.
TACE is particularly useful for patients who are not candidates for surgery or liver transplantation.
Q4: What are the benefits of TACE?
A: The benefits of TACE include:
- Targeted treatment: TACE delivers high concentrations of chemotherapy directly to the tumor, reducing the impact on the rest of the body.
- Minimally invasive: The procedure is less invasive than surgery, with a shorter recovery time.
- Effectiveness: TACE can significantly shrink tumors, control cancer growth, and improve survival rates, particularly in liver cancer patients.
- Combination with other treatments: TACE can be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as surgery, radiation therapy, or systemic chemotherapy.
Q5: How is TACE performed?
A: The TACE procedure involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The patient is given local anesthesia and sometimes sedation. Imaging tests, such as angiography, are used to guide the procedure.
- Catheter insertion: A catheter (a thin tube) is inserted through a small incision in the groin and guided through the blood vessels to the hepatic artery, which supplies the liver tumor.
- Chemotherapy delivery: Chemotherapy drugs are injected directly into the artery feeding the tumor.
- Embolization: Tiny particles are injected to block the artery, trapping the chemotherapy in the tumor and cutting off its blood supply.
- Aftercare: The catheter is removed, and the patient is monitored for a few hours before being allowed to go home, usually the same day or the next day.
Q6: What are the potential side effects of TACE?
A: While TACE is generally safe, there are some potential side effects, including:
- Post-embolization syndrome: A common side effect that includes fever, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and abdominal pain. These symptoms typically resolve within a few days.
- Liver dysfunction: There is a risk of liver damage, particularly in patients with pre-existing liver disease.
- Infection: Although rare, there is a risk of infection at the catheter insertion site or in the liver.
- Bleeding: There is a small risk of bleeding at the catheter insertion site or internally.
Your healthcare team will monitor you closely during and after the procedure to manage any side effects.
Q7: How do I know if TACE is the right treatment for me?
A: Whether TACE is suitable for you depends on several factors, including the size and location of your tumor, the overall function of your liver, and your general health. TACE is often considered for patients with liver tumors that cannot be surgically removed or who are awaiting a liver transplant. Your oncologist will evaluate your specific situation and discuss whether TACE is a good option for you.
Q8: What can I expect after TACE treatment?
A: After TACE, you may experience some side effects, such as fatigue, fever, and abdominal pain, which are usually temporary. Most patients can return to normal activities within a week. You’ll have follow-up appointments and imaging tests to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and to check for any signs of recurrence. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions on how to care for yourself after the procedure.
If you have more questions about Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) or are considering it as a treatment option, talk to your healthcare provider. They can provide detailed information and help you understand how TACE might fit into your overall cancer treatment plan.
Related Post

CyberKnife
August 6, 2024
Immunotherapy
August 7, 2024
MRI Linac
August 7, 2024
Gamma Knife
August 7, 2024
Cancer Screening
August 22, 2024
Gallery
Click below to book a clinic appointment
Ask More Questions Send Query On Email